What is Physiotherapy?
A Chartered Physiotherapist has been trained to degree level in anatomy, physiology and pathology. Physiotherapists are therefore specialists in treating joint, spinal or soft tissue injuries including muscle or ligament strains/sprains. Physiotherapists work on injuries and medical conditions by correcting and improving the body's natural healing mechanisms.
Common conditions treated include:
 Back pain
Back pain
4 in 5 adults will experience back pain at some point in their lives and it is more prevalent between the ages of 35-55. Unfortunately a percentage suffer with recurrent and persistent chronic back pain. Physiotherapy is beneficial for acute back pain and can prevent recurrence. It can also assist in the management of more chronic pain.
 Sciatica
Sciatica
Sciatic pain is typically felt as pain/burning radiating through the buttock, the back or side of the leg and into the foot. It can be associated with pins and needles or numbness. It is commonly caused by compression of the nerve, either from a prolapsed disc or degenerative changes.
 Neck pain
Neck pain
Neck pain has many causes including poor posture, spondylosis (degeneration of the vertebral joints and disc), muscle tension and joint/ligament strains.
 Headaches
Headaches
Headaches can be related to movement disturbances in the neck or tension in the muscles between the head and neck.
 Whiplash injuries
Whiplash injuries
Common symptoms following a whiplash injury include pain in the head, neck and upper thorax, dizziness, arm pain/weakness, low back pain, jaw pain and visual disturbances. Physiotherapy is particularly beneficial to encourage healing, reduce pain and prevent chronicity.
 Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Also known as degenerative arthritis or degenerative joint disease. Symptoms may include joint pain, stiffness, tenderness and swelling. Exercise therapy can alleviate the pain and stiffness and increase function. It can also be beneficial to strengthen the muscles around the joint prior to joint replacement.
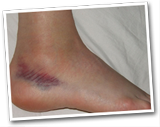 Sprained ankles
Sprained ankles
A common injury where one or more of the ligaments around the ankle are overstretched or torn. Symptoms include swelling, bruising, pain, reduced movement and difficulty walking or weight-bearing.
 Tennis elbow
Tennis elbow
This is an inflammation of the outer elbow where the tendon attaches to the bone. It is commonly caused by repetitive movements and gripping, e.g. when playing racquet sports, but can develop with other activities of daily living. Your physiotherapist will treat the condition and advise on modifications to prevent recurrence.
 Frozen shoulder
Frozen shoulder
This is a disorder in which the capsule (connective tissue surrounding the joint) becomes inflamed and tight, greatly restricting movement and causing pain. The pain is often constant, worse at night and can severely restrict the function of the arm. Physiotherapy can help to restore and maintain the movement, and alleviate the pain.
 Repetitive strain injury
Repetitive strain injury
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) is an umbrella term for an occupational overuse syndrome that affects nerves, tendons and muscles. The aim of physiotherapy is to restore normal function to the tissues that are affected. Ergonomic advice is also provided to help with the condition.
 Sports injuries
Sports injuries
Few people doubt the beneficial effects of sport on their fitness and well-being. Sports Injuries occur as a result of physical activities carried out either for general recreational purposes or with more professional goals in mind. They may be caused by accidents or by overuse, and they do not necessarily differ from injuries sustained in non-sporting activities. The injury can be treated effectively with physiotherapy to ensure optimal healing and speedy return to activities.
Listed above are the more common conditions but physiotherapy is beneficial for many other, less easily recognised problems. Please contact the clinic to discuss these further.